The Storage Form of Glucose in Humans Is
Storing glucose in plants. The form of glucose used for storage in animals is glycogen.
Is the storage form of glucose in plants.

. This is mostly made in the liver andor muscle cells. The liver performs the most important storage mechanism of glucose. It represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
The liver is a site of glucose neo-genesis or gluconeogenesis not glucose storage. This polysaccharide is the storage form of glucose in the human body. Glycogen is synthesized and stored mainly in the liver and the muscles.
Fiber continues to the large. The form of storage used in plants is starch. The liver not only releases glycogen when needed but also regulates the amount of glucose already present in your bloodstream.
Order the steps of carbohydrate digestion. A substantial amount of the glucose that is metabolized to produce energy for muscle contraction during exercise is stored in the form of glycogen in the cells of the liver and. While every person is unique the average carbohydrate storage capacity in the body roughly breaks down as follows.
2 pts soluble and insoluble 4. The glucose units in this polysaccharide are joined only by a-14-glycosidic bonds. The energy from the sunlight is used to make energy for the plant.
Glycogen is synthesized and stored mainly in the liver and the muscles. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body. The liver is the largest organ in the body and can contain up to 10 of its volume in glycogen.
In humans glycogen is made and stored primary in the cells of liver and the muscles hydrated with three or four parts of water. Again the liver stores glucose in the form of glycogen. Because glucose can be metabolized rapidly and the resulting energy can be used by cells glycogen is an important energy-storage molecule.
In humans glycogen is made and stored primarily in the cells of the liver and skeletal muscle. Photosynthesis occurs in light photo light such as when the sun is shining. _ the storage form of glucose in humans and animals is stored in the and cells.
Blood plasma contains the most glucose mobilized glucose and useable glucose. Consequently how much carbohydrates are stored in the body. Liver provides glycogen from.
The storage form of glucose in plants is starch. Starch it please. Maltose and other disaccharides are broken down to monosaccharides and absorbed into blood b.
Glycogen Which blood glucose lab value is considered a positive test indicative of diabetes mellitus. Glycogen is as an important energy reservoir. D None of the above.
The storage form of glucose in animals including humans is _____. The glucose units in this polysaccharide are joined by B-14-glycosidic bonds. Starch is a polysaccharide.
This polysaccharide is the structural component of plant cell walls and cannot be digested by humans. The Storage Form Of Glucose In The Body Is Glycogen Thus glucose becomes available to supply energy to the brain and other tissues regardless of whether the person has eaten recentlyThe liver stores about one-third of the bodys total glycogen and releases glucose into the bloodstream as needed. Whether from liver stomach or intestines glucose goes to blood first.
When energy is required by the body glycogen in broken down to glucose which then enters the glycolytic or pentose phosphate pathway or is released into the bloodstream. Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals fungi and bacteria. Excess glucose beyond what the body needs for immediate energy is converted into glycogen a storage form of carbohydrate or converted into fat and stored in body fat cells.
Glycogen is a large branched polysaccharide that is the main storage form of glucose in animals and humans. Glycogen is the main storage form of glucose in humans. Glycogen is multi-branched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals and fungi.
The storage form of glucose in animals is. The leaves of a plant make sugar during the process of photosynthesis. Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in animals and humans which is analogous to the starch in plants.
Structurally glycogen is very similar to amylopectin with alpha acetal linkages however it has even more branching and more glucose units are present than in amylopectin. Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in animals and humans which is analogous to the starch in plants.

Yeast Two Hybrid System For Protein Protein Interaction Studies Interactive Yeast Study
Glucose Regulation And Utilization In The Body

Carbohydrates Openstax Biology

Glycogen An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

How The Body Decreases Blood Glucose Concentrations After Eating
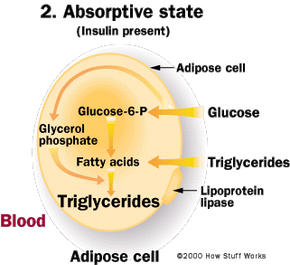
Fat Storage How Fat Cells Work Howstuffworks

Glycogenolysis Biochemistry Britannica

How The Body Decreases Blood Glucose Concentrations After Eating

Glycogenolysis Biochemistry Britannica

Study Student Studyblr Studying Studygram Notes Science Muji Mujipens Mujinotebook Notes Inspiration Studyblr Notes Study Notes

Glycogen And Diabetes Role Storage Release Exercise

Reading Structure And Function Of Carbohydrates Biology I

Pyrimidine Catabolism Ump And Cmp Degradation Pathway Covalent Bonding Pathways Animal Cell

Part 4 Tissues Centre Of Excellence Anatomy And Physiology Medical Anatomy Human Anatomy And Physiology
Glucose Regulation And Utilization In The Body

These Are Both Storage Polysaccharides And Carbohydrates Starches And Glycogen Form Helices In Unbranched Regions Be Human Liver Carbohydrates Large Intestine


Comments
Post a Comment